Words to Know - A POI Glossary
What is POI?
For Parents of Daughters with Galactosemia and POI
For Women with Galactosemia and POI
Other Resources
This glossary explains words used in the Guide to Galactosemia and Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI).
Amenorrhea [ey-men-uh-ree-uh]: A word used to describe when a woman’s menstrual period is not normal. Primary amenorrhea describes when a woman’s period does not start when it should (by 15 years of age). Secondary amenorrhea describes when a woman’s period stops after she has already had it several times.
Estradiol [es-truh-dahy-awl]: An important form of estrogen. It plays a role in the growth of the female uterus and vagina. It also helps breast development.
Estrogen [es-truh-juhn]: This is a word for several female sex hormones, such as estradiol, that are made by the ovaries. A lack of estrogen can cause health problems like heart disease and osteoporosis.
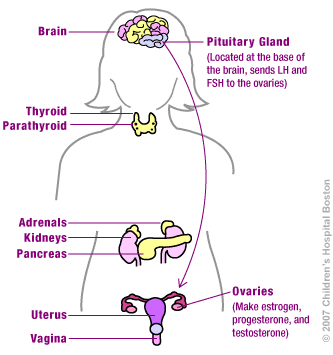
Follicle Stimulating Hormones (FSH) [fol-i-kuhl stim-yuh-lat-ing hawr-mohn]: This is a hormone released by the pituitary gland when the brain senses that not enough estrogen is being made. Women with POI tend to have a high FSH level since their ovaries are not able to respond to FSH and produce estrogen.
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT) [gam-eet in-tra-fuh-lop-i- an trans-fur]: A medical procedure where a woman’s egg is placed in one of her fallopian tubes with a man’s sperm.
Gonads [goh-nads]: This is a word for the reproductive glands found in humans. The female gonad is called the ovary. The ovary is one of a pair that produces eggs and releases hormones like estrogen. Hormone [hawr-mohn]: A chemical or substance in the body that controls the activities of certain parts of the body.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) [hawr-mohn ri-pleys– muhnt ther-uh-pee]: Hormone replacement therapy is a medicine that a woman with POI takes to replace the estrogen and other hormones her body is not producing naturally. There are many forms of hormone replacement therapy, including pills, patches, shots, and vaginal rings.
Hypothalamus [hahy-puh-thal-uh-muhs]: An area of the brain that controls things like sleep patterns, hunger, and body temperature by producing hormones, including one that regulates FSH release.
Infertility [in-fur-til-i-tee]: The diminished ability to become pregnant and have a child. It is also defined as the inability to become pregnant after a year of regular intercourse without birth control.
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) [in-vee-troh fur-tl-uh-zey-shuhn]: A medical procedure that occurs in a lab where a sperm is placed in a petri dish with a woman’s egg. The fertilized egg is then inserted into a woman’s uterus.
Osteoporosis [os-tee-oh-puh-roh-sis]: Osteoporosis is a disease in which the bones become weak and are more likely to break. People with osteoporosis most often break bones in the hip, spine, and wrist. Estrogen is important to build strong bones. It is important that women with POI receive HRT to reduce their chances of osteoporosis.
Ovary [oh-vuh-ree]: This is the female gonad. The ovary is one of a pair of reproductive glands in women. They are located in the pelvis. The ovaries produce eggs (ova) and female hormones.
Pre-menstrual Syndrome (PMS) [pre-men-stroo-uhl sin-drohm]: A combination of physical and mood disturbances that happen before a woman’s period. Symptoms can include breast tenderness, bloating, and psychological changes such as anger and depression.
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI) [prahy-mer-ee oh-vair-ee-uhn in– suh-fish-uhn-see]: POI (sometimes called premature ovarian failure or POF) is a term used by doctors when a woman is under 40 and her ovaries are not working normally. This means that her ovaries are not making estrogen and other hormones that are important to her health. Galactosemia is one of the few known causes of POI. About 1 in 1,000 women in the United States under the age of 29 have POI. Most women with POI do not know what caused it.
Uterus [yoo-ter-uhs]: A hollow organ found in a woman’s lower abdomen. This is where a fertilized egg implants and grows. It is also called a womb.